Rubber Magnets: An Introduction
What Are Rubber Magnets?
Flexible Rubber Magnetic Sheets, or magnetic rubber, are a composite of abiogenic ferrite along with rubber or plastic/rubber binders. They have a lot going for them: They’re versatile — you can bend, twist and cut them without affecting their magnetism.
Rubber magnets made their first commercial appearance in the mid-20th century, as industries sought a cheap and malleable magnetic alternative. Over several decades, their applications have expanded from advertising to the automotive industry.

How Are Rubber Magnets Made?
Rubber Magnets: Material Used
The magic recipe? Ferrite powder (such as strontium or barium ferrite) and rubber or plastic binder—usually NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) or CPE (Chlorinated Polyethylene) to hold the ferrite powder in a reconstituted form. That one-two punch is only as strong as the combo between them.
The Manufacturing Process
The magnetic powder is mixed with rubber or plastic well at the initial stage. The blend produced is subsequently converted into sheets or extruded into moldable forms. These are magnetic through the application of a strong magnetic field, are cut to their finished size, and, in some cases, are laminated.
Types of Rubber Magnets
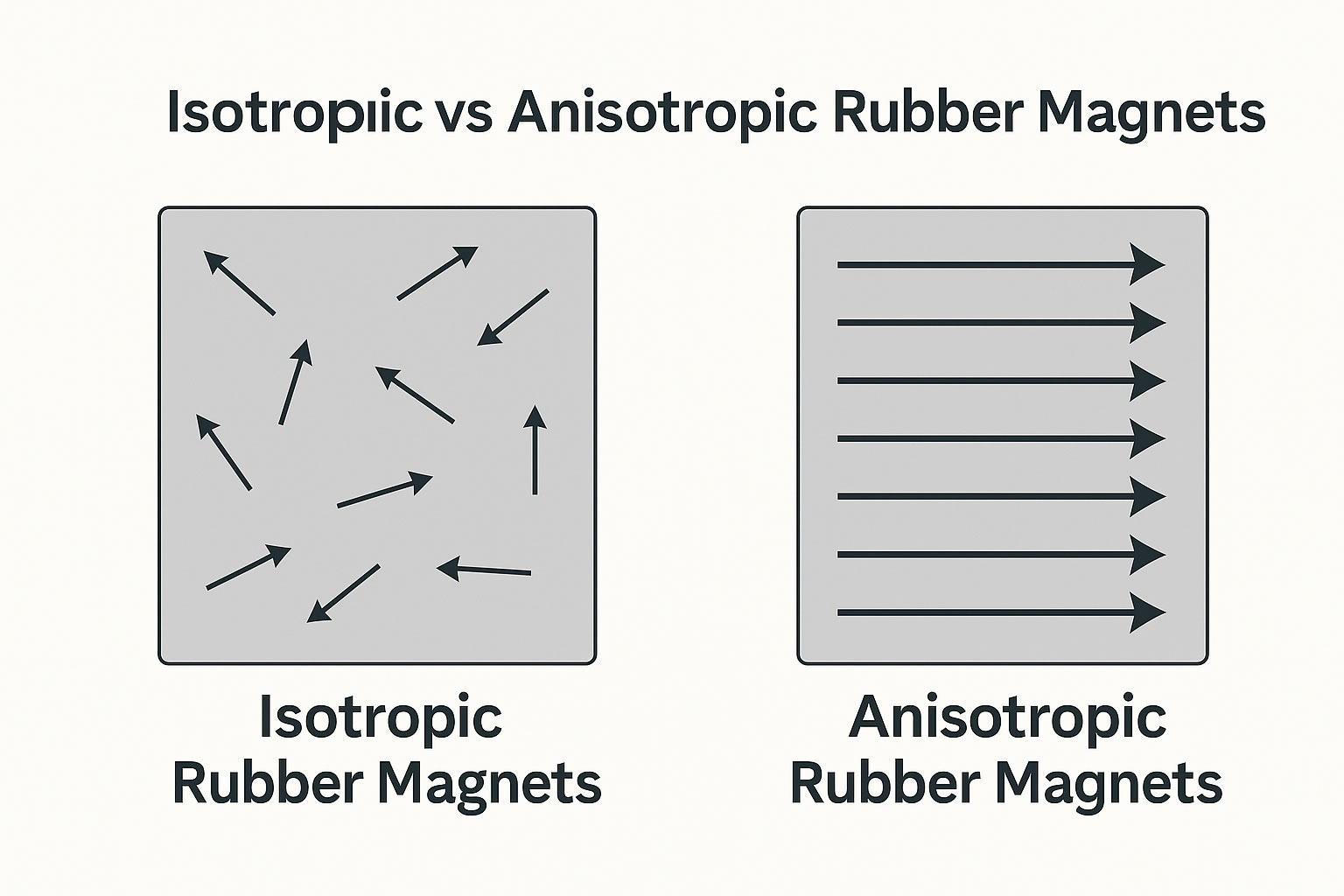
Isotropic vs Anisotropic Rubber Magnets
Isotropic: Multiple poles are magnetised in several directions, easier and cheaper to produce, but weaker in magnetic strength.
Anisotropic: Magnetised in one direction, for the strongest magnetic properties, a little more expensive.
Flexible Rubber Magnets
These are the classic rubber magnets, which can be bent or twisted without damaging their magnetic properties, and are the best value magnets on the market.
Printable Rubber Magnets
Need marketing materials? These magnets come preprinted, with a surface perfectly designed for custom print advertising.
Properties of Rubber Magnets

Magnetic Strength
Although not as strong as rare-earth magnets, they are still powerful enough for most light-duty holding needs, such as holding papers to the surface of a refrigerator, minor signs or other displays on a steel wall or ceiling, or attaching light objects.
Flexibility and Durability
You can roll, twist, and bend rubber magnets without damaging them. And, they resist corrosion miles better than their metallic cousins.
Temperature Resistance
Most rubber magnets can operate at temperatures between -20°c and 80°c, depending on the specific material. And some can even exceed that temperature.
Application for Soft Magnetic Rubber Magnet
Industrial Uses
Car door gaskets and seals—or motor parts in which a light magnetism is necessary—might use rubber magnets.
Commercial uses and advertising
Car magnets, business card magnets, magnetic signs, point-of-purchase displays — rubber magnets are the star of advertising!
Educational and DIY Projects
Rubber magnets are a favourite for classrooms and hobbyists. From magnetic learning boards to homemade refrigerator art, the options are endless.
Advantages of Rubber Magnets
Cost-Effectiveness
Neodymium or samarium-cobalt magnets are far more expensive than rubber magnets for mass production use cases, but they significantly reduce costs.
Easy Customization
You can cut them easily with scissors or a utility knife, and they’re available in different colors, thicknesses and shapes.
Safe Handling
No harder or stronger than 3″x 1/16″ thick, no heavy metals, truly child safe and friendly!
Limitations of Rubber Magnets
Weaker Magnetism: It is weaker than other magnets.
If what you need is a magnet to pin up a heavy object, rubber magnets might not be your best bet. They are suitable for light-duty tasks.
Environmental Considerations
While robust, rubber magnets aren’t the most environmentally friendly choice. Disposal can be difficult unless manufacturers use recyclable materials.
How to Select the Proper Rubber Magnet
Application-Based Selection
So, first question: what do you want to use it for? Lightweight signage? A motor part? You will need to decide the size, power, and type, depending on what you will use your application for.
Length, Width, and Strength Aspects
A greater surface area means more holding power. Thicker magnets tend to be stronger but less flexible, so choose one based on your needs.
How to care for and store the rubber magnets
Best Practices for Longevity
- Keep them flat so they don’t get creased.
- Avoid extreme heat.
- Clean periodically to preserve surface adhesion.
- By using maintenance and cleaning tips, you can make them last!
Trends in Rubber Magnets to Come
Eco-Friendly Materials
Manufacturers are developing biodegradable plastics and recycled ferrite powders to produce more environmentally friendly rubber magnets.
Technological Innovations
Thanks to advances in stronger composite materials and multipurpose coatings, tomorrow’s rubber magnets could be capable of things that surprise us.
FAQs
Are rubber magnets waterproof?
Yes! Most rubber magnets are inherently water-resistant, but laminated types offer extra protection for outdoor use.
Can rubber magnets lose their strength over time?
Yes, especially if exposed to high temperatures or strong opposing magnetic fields, but under normal conditions, they last for years.
Are rubber magnets safe for children?
Absolutely! They’re soft, flexible, and free of sharp edges, making them ideal for educational and craft purposes.
How do you cut rubber magnets?
Simple household scissors or a utility knife will do the trick. Just mark your cutting lines clearly for neat results.
What is the maximum temperature rubber magnets can handle?
Most standard rubber magnets can withstand temperatures up to 80°c (176°f). Special formulations can tolerate even higher temperatures if needed.






