Let’s be honest — magnets aren’t just for fridges anymore. You’ve likely come across neodymium magnets if you’re in manufacturing, automation, or electronics. Among the various grades, N35 magnets are the entry point — affordable, reliable, and surprisingly robust. This guide will walk you through everything you need about N35 magnets and how to use them smartly in your industrial setup.
Understanding the Basics of N35 Magnets
What Does “N35″ Actually Mean?
The “N” stands for Neodymium, and the number “35″ refers to the magnet’s maximum energy product, measured in mega Gauss Oersteds (MGOe). N35 indicates a value of around 35 MGOe, which defines how much magnetic energy the magnet can deliver.
The Composition: Neodymium, Iron, and Boron
These magnets belong to the NdFeB family — a mix of Neodymium (Nd), Iron (Fe), and Boron (B). This combination forms the strongest type of permanent magnets available commercially.
How Are They Made?
Manufacturing involves sintering fine alloy powder into a solid block, followed by magnetization in a high-energy magnetic field. Precision shaping and coating are done afterward.
Key Properties of N35 Magnets
Magnetic Strength and Pull Force
Although N35 is on the lower end of the neodymium magnet scale, it’s still much stronger than ceramic or alnico magnets. A small N35 disc can hold several pounds of weight.
Resistance to Demagnetization
N35 magnets maintain their magnetism under normal industrial conditions. However, extreme heat or strong opposing magnetic fields can affect performance.
Thermal and Environmental Stability
They operate effectively up to 80°C (176°F). Beyond that, performance starts to drop unless they’re specially modified.
Advantages of Using N35 Magnets in Industry
Cost-Effectiveness
They’re cheaper than higher grades like N42 or N52, making them ideal for applications without ultimate strength.
High Energy Product
Despite being a lower grade, N35 still offers excellent magnetic power compared to alternatives like ferrite or samarium-cobalt.
Versatility Across Applications
From holding tools in place to sensors and electric motors, N35 magnets deliver consistent performance across use cases.
Common Industrial Applications of N35 Magnets
Electric Motors and Generators
Used in compact, efficient designs where medium power output is sufficient.
Magnetic Separation Systems
Perfect for separating ferrous materials from bulk flow or powders.
Magnetic Holding and Lifting
Ideal for creating magnetic jigs, tool holders, and work-holding systems.
Sensors and Instrumentation
Works with Hall-effect sensors in positioning and rotational speed systems.
Medical Devices
Used in drug delivery, MRI components, and surgical tools, though coatings are critical here.
N35 vs Higher Grades: Why Choose N35?
Cost vs Performance Balance
Higher grades (N42, N52) give more power but cost more. If you don’t need extreme strength, N35 saves money.
Comparison Snapshot
| Grade | Max Energy Product | Max Temp | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| N35 | ~35 MGOe | 80°C | Low |
| N42 | ~42 MGOe | 80–100°C | Mid |
| N52 | ~52 MGOe | 60–80°C | High |
When N35 Is the Right Fit
Best for general-purpose applications, where moderate strength and cost control matter more than maximum pull.
Limitations of N35 Magnets
Lower Temperature Limit – Starts losing strength above 80°C.
Corrosion Risk – Exposed magnets rust easily in humid environments.
Coatings and Surface Treatments
Why Coatings Are Essential
Without protection, neodymium magnets oxidize and break down quickly.
Common Coating Types
Ni-Cu-Ni (Nickel-Copper-Nickel) – Most widely used, silver finish
Epoxy – For high-humidity or marine environments
Zinc – Budget option with fair protection
Safety Precautions When Handling N35 Magnets
Avoid Finger Pinches – Even small N35 magnets snap together violently
Keep Away from Electronics – Can interfere with pacemakers or magnetic storage
Use Protective Gear – Especially during machining or assembling
🔩 Table: Magnetization Directions for N35 Magnets
| Magnet Shape | Typical Dimensions | Axial Magnetization | Diametrical Magnetization | Radial Magnetization | Multipole Magnetization | Notes / Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disc / Cylinder | D x H (e.g., 10×2 mm) | ✅ Common | ✅ Optional | 🚫 Rare | ✅ Ring versions only | Axial: Poles on flat faces; Diametrical: Poles on sides |
| Ring | OD x ID x H (e.g., 20×10×5) | ✅ Common | 🚫 Uncommon | ✅ Available | ✅ Often used | Radial for motors; Multipole for encoder rings |
| Block / Cube | L × W × H (e.g., 10×10×5) | ✅ Common (thickness) | ✅ Optional (width) | 🚫 Not used | 🚫 Rare | Magnetization direction should be specified (e.g., along X) |
| Sphere | Diameter (e.g., 8 mm) | ✅ Center-to-surface | 🚫 Not applicable | 🚫 Not applicable | 🚫 Not practical | Treated as dipole across any diameter |
| Arc / Segment | Custom | ✅ (Through thickness) | 🚫 Not typical | ✅ Used in motors | ✅ Custom possible | Common in BLDC motors, radially magnetized segments |
| Cylinder (Long) | Length ≥ 3× diameter | ✅ Along length | ✅ Across diameter | 🚫 Rare | 🚫 Rare | Needle magnets, sensors |
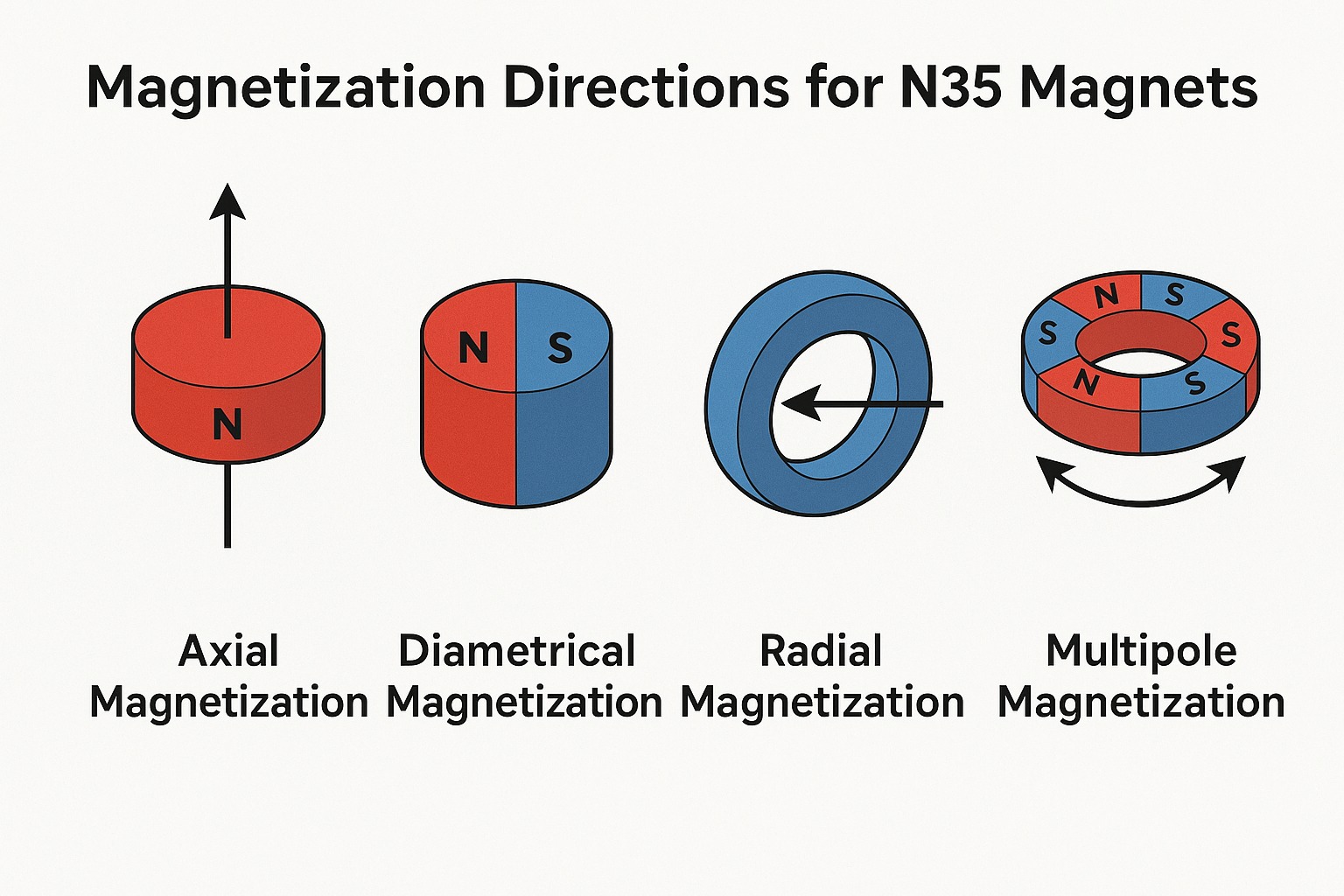
Magnetization Types Explained
Axial Magnetization: Magnetic poles on flat ends (top and bottom). Most common.
Diametrical Magnetization: Poles on curved sides (like left and right).
Radial Magnetization: North and south poles radiate from or toward the center (used in rings).
Multipole Magnetization: Multiple N-S poles on a single surface (encoder rings, rotating sensors).
Example Use Cases
Axially magnetized discs: Used in sensor mounting, closures, and general-purpose assemblies.
Radially magnetized rings: Ideal for motors and generators (more efficient magnetic flux).
Multipole magnetized rings: Used in encoders and rotation tracking systems.
📊 Table: Shapes and Sizes of N35 Neodymium Magnets
| Magnet Shape | Common Sizes (mm) | Typical Magnetization | Available Grades | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disc / Cylinder | Ø5×1, Ø10×2, Ø15×3, Ø20×5, Ø25×10 | Axial / Diametrical | N35 – N52 | Sensors, crafts, closures, speakers |
| Block / Cube | 5×5×5, 10×10×2, 20×10×5, 50×25×10 | Axial (L/W/H) | N35 – N52 | Holding systems, motors, DIY, magnetic locks |
| Ring | Ø10×5×2, Ø20×10×5, Ø30×15×10, Ø50×30×10 | Axial / Radial / Multipole | N35 – N52 | Motors, generators, rotating sensors, encoders |
| Sphere | Ø3, Ø5, Ø8, Ø10 | Axial (dipole) | N35 – N48 | Magnetic toys, displays, scientific models |
| Arc Segment | Custom: R20×R15×7.5×20°, R50×R45×10×30° | Radial / Axial | N35 – N42 | BLDC motors, MRI systems, rotating equipment |
| Rod / Bar | Ø4×20, Ø6×30, 5×5×50 | Axial (length) | N35 – N42 | Sensors, levitation, linear actuators |
| Countersunk Disc | Ø20×5 (M3 hole), Ø25×5 (M4 hole) | Axial | N35 – N50 | Wall mounting, fixture installations |
| Cylinder with Hole | Ø20×5×Ø5, Ø30×10×Ø10 | Axial / Radial | N35 – N48 | Mounting applications with bolt support |
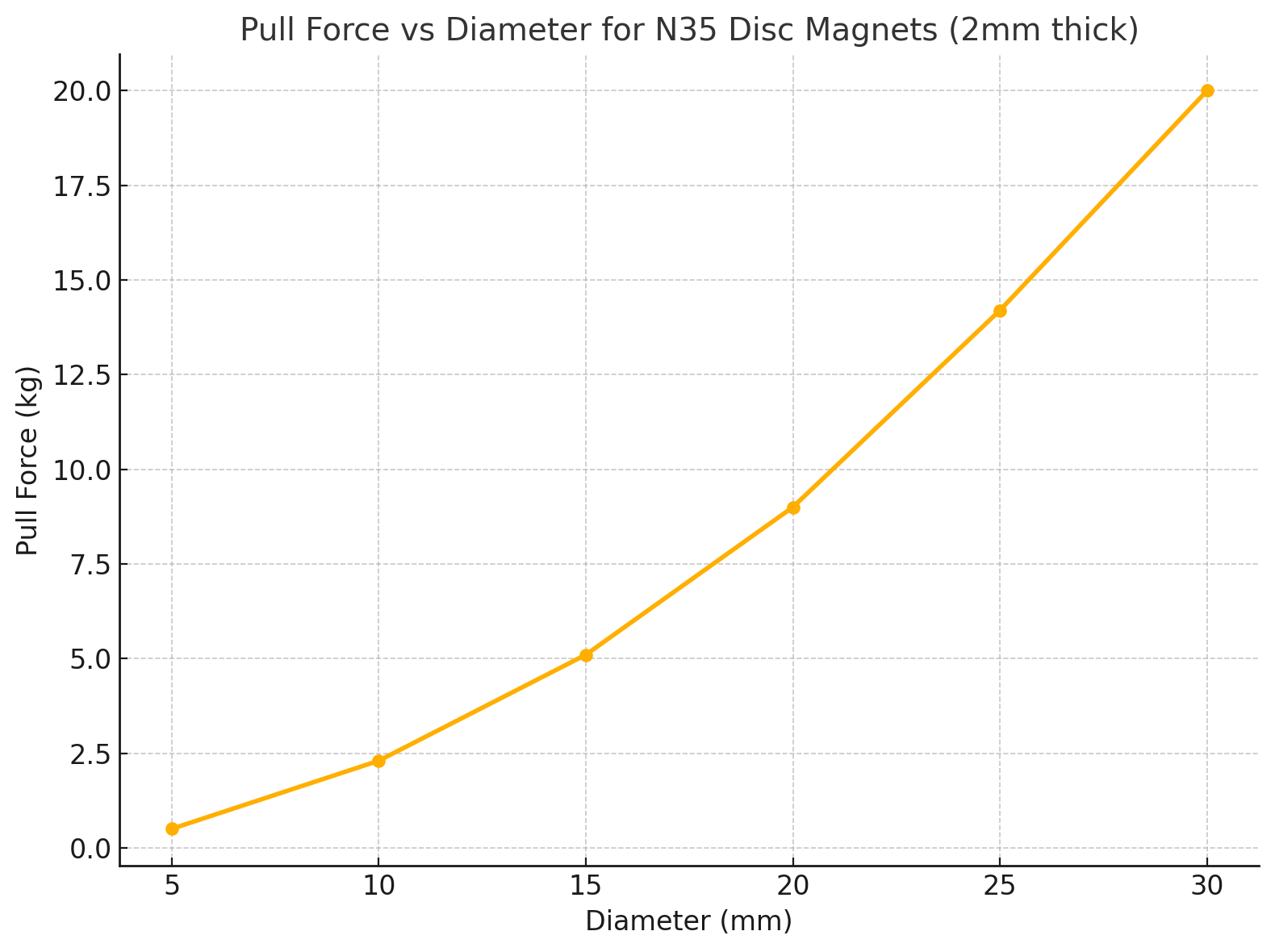
The comparison chart shows how the pull force increases with magnet diameter for N35 disc magnets with a fixed thickness of 2 mm. As the diameter increases, the magnetic pull force grows significantly, making size selection critical for strength-sensitive applications.
Key Notes on Sizes & Customization
Small N35 magnets (under 10 mm) are used for precision electronics and crafts.
Large sizes (50 mm and above) are typically custom ordered for high-strength applications like wind turbines or lifting tools.
Thickness (H) often affects pull force and flux density — a thicker magnet generally means stronger holding power.
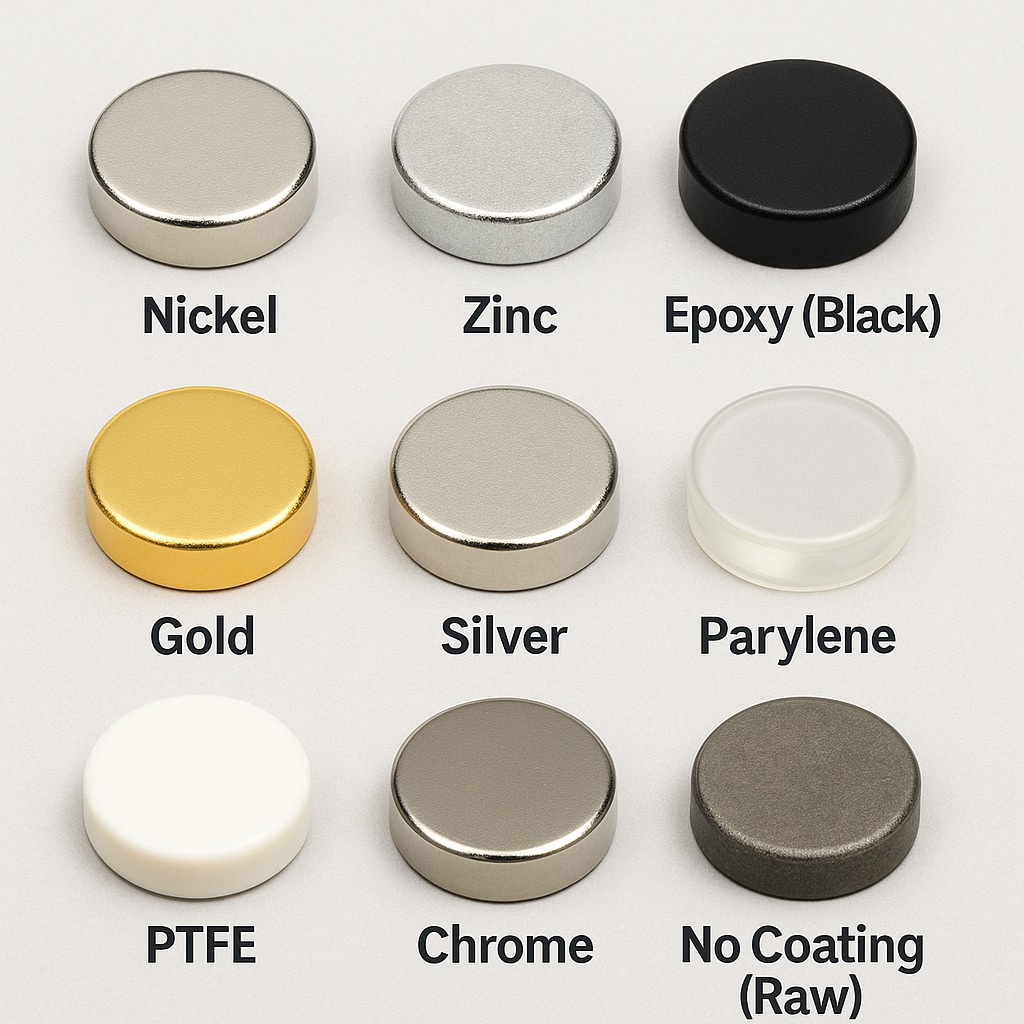
Table: Coatings Used on N35 Magnets
| Coating Type | Material | Appearance | Corrosion Resistance | Durability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Copper-Nickel (Ni-Cu-Ni) | Triple layer (Ni+Cu+Ni) | Shiny silver | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | General-purpose magnets, electronics, enclosures |
| Zinc (Zn) | Zinc metal | Dull gray/silver | ⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Cost-sensitive applications, temporary setups |
| Epoxy (Black) | Epoxy resin | Black matte | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Harsh environments, marine, automotive, humid areas |
| Gold (Au) | Gold plating over Ni-Cu-Ni | Gold shiny | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | Medical tools, jewelry, decorative uses |
| Silver (Ag) | Silver plating over Ni-Cu-Ni | Bright silver | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | Antimicrobial surfaces, medical sensors |
| Parylene | Polymer layer | Clear, thin transparent | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | Medical implants, aerospace, electronics |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Polytetrafluoroethylene | White or translucent | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Chemical labs, high-friction surfaces |
| Chrome (Cr) | Chromium | Shiny metallic | ⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | Aesthetic or light wear protection |
| Plastic/Polymer Coating | Molded plastic | Various colors | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Flexible) | Educational magnets, toys, child-safe applications |
| No Coating (Raw) | None | Dark gray metallic | ⭐ (Very Low) | ⭐⭐ (Poor) | Must be sealed; used for prototyping only |

Important Notes
Ni-Cu-Ni is the most common coating, providing a balance of cost, protection, and appearance.
Epoxy-coated N35 magnets are recommended for outdoor or wet environments.
Parylene and PTFE are used in specialized industries where biocompatibility or chemical resistance is critical.
Raw neodymium magnets corrode quickly and are unsuitable for most open-air or moist environments.
Buying Guide: What to Look For
Grade & Dimensions – Always double-check specs
Shape & Magnetization – Axial, diametric, or radial
Coating Type – Based on your application environment
Customizing N35 Magnets for Specific Use Cases
Shapes – Discs, rings, blocks, arcs
Custom Magnetization – Multi-pole, radial, or segment-based
Integrated Assembly – Embedded into plastic or metal housings
Storage and Maintenance Tips
Keep Away from Heat
Use Dry, Cool Storage
Avoid Mechanical Shocks
Recycling and Environmental Concerns
Can N35 Magnets Be Recycled?
Yes — specialized facilities can recover rare earth elements.
Responsible Disposal
Don’t toss in general waste. Partner with recycling vendors or manufacturers offering take-back programs.
Case Studies and Real-Life Use Examples
N35 in Electric Vehicles
Used in motor control units and sensor arrays.
N35 in Automation Equipment
Keeps robotic arms in place and secures tooling quickly and reliably.
N35 magnets are an excellent entry point for industries looking for cost-effective magnetic power. They may not be the strongest neodymium option, but they pack a punch far beyond traditional magnet types. With innovative applications, coatings, and care, they can become a long-term asset in your operations.
FAQs
1. Can N35 magnets damage electronics?
Yes, they generate strong fields that can disrupt sensitive electronics. Keep them at a safe distance.
2. Are N35 magnets safe for medical use?
Only if properly coated and used in compliance with medical device standards.
3. How long do N35 magnets last?
With proper care and environment, they can retain magnetism for decades.
4. What is the difference between N35 and ceramic magnets?
N35 magnets are 10x stronger than typical ceramic magnets of the same size.
5. Where can I buy N35 magnets in bulk?
Check industrial magnet suppliers or manufacturers specializing in neodymium products with customization options.






